Anyone who thinks additively will get further layer by layer
Additive manufacturing, also known colloquially as 3D printing, is a generic term that encompasses a variety of different 3D printing processes. What all processes have in common is that components are built up in layers.
Thanks to the rapid development of this manufacturing technology, additive manufacturing is now also suitable for the production of end products.
Compared to conventional manufacturing processes, it opens up new design freedoms in particular, which can be used, for example, in the optimization of lightweight construction, functional integration or variant production.
Overview of advantages
Variant manufacturing
Is this component also available in a different size? Variant production is no longer a problem thanks to additive manufacturing. Where previously new tools had to be created or programs changed, today it is sufficient to adapt the 3D CAD model.
Integration of functions
All components fulfill a function. Thanks to additive manufacturing, many functions can be integrated directly into the part. For example, fluid channels, latching functions or various motion sequences can be implemented at no extra cost.
Consolidation of assemblies
Complex systems consist of many components – additive manufacturing makes it possible to combine several components into one part. This reduces costs along the entire process chain.
Unlimited freedom of form & complex structures
Undercuts, curved holes, free-form surfaces.
Additive manufacturing opens up completely new design possibilities. This allows products to be optimized in terms of design and functionality.
Speed due to tool-less production
Series production can begin immediately. There is no need for time-consuming tool production and tool testing, which significantly reduces time-to-market.
The production plants
State-of-the-art manufacturing facilities
Whether it is an individual one-off item or profitable series production – thanks to state-of-the-art production facilities and different manufacturing processes, we are able to respond to the needs of our customers.
Filigree components with highly complex structures, precision-fit moulds or intelligent design and functional principles – We are the right partner for you.
We have specialised in FFF, INKJET and MULTI-JET processes and are thus prepared for many industries and areas of application.
Application examples
Multi Jet Fusion
The HP MJF process is based on a powder bed-based additive manufacturing method. It starts with a thin layer of powdered material, typically polyamide (nylon).
A print head applies two types of liquids (agents) to the powder bed:
1. fusing agent: this liquid is applied where the powder is to be fused.
2. detailing agent: This liquid is applied to the edges of the areas to be fused to ensure sharp and precise edges.
Once the agent has been applied, the powder is heated with an infrared lamp.
The fusing agent absorbs the heat and fuses the powder into a solid material, while the detailing agent ensures that the edges remain precise. This process is repeated layer by layer until the complete object is built up.
Advantages
Speed
As the print head can process large areas simultaneously, the process is significantly faster than many other 3D printing methods.
Cost efficiency
Due to the efficient use of materials and the fast production time, the manufacturing costs per part are often lower than with conventional production methods.
Variety of materials
In addition to polyamide, other materials such as flexible plastics and high-performance polymers can also be used



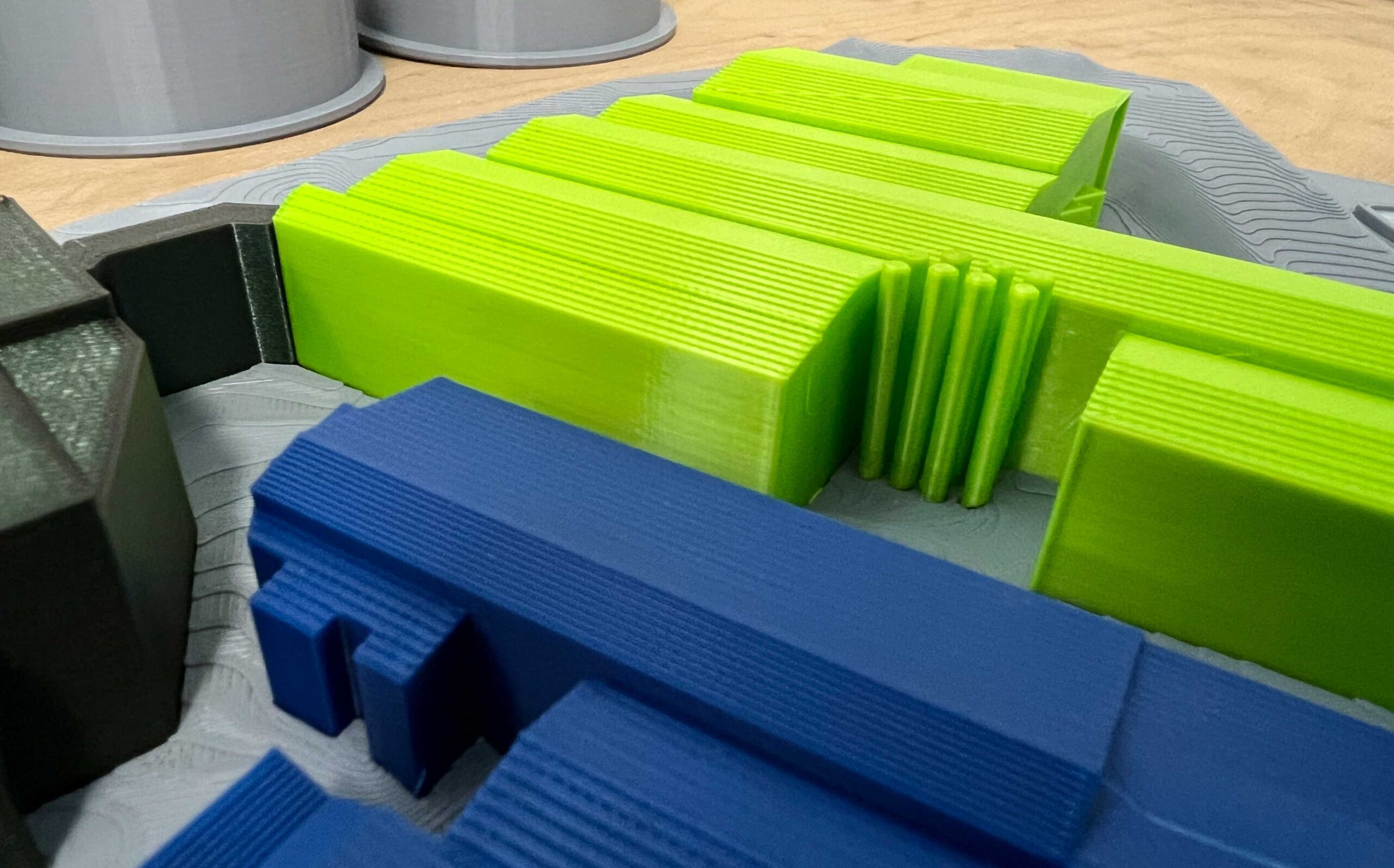
FDM – Fused Deposition Modeling
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) is a widely used process in the field of 3D printing that is based on the layer-by-layer production of three-dimensional objects.
In fused deposition modeling, a thermoplastic plastic wire, known as filament, is melted through a heated nozzle. This nozzle moves in a precisely controlled manner along the X and Y axes and deposits the molten material layer by layer onto a build platform. After cooling, the material solidifies and forms a solid layer. This process is repeated layer by layer until the entire object is completed.
Advantages
Diversity
A wide range of colors and materials is available
Manufacturing costs
The materials are comparatively inexpensive, which also makes the products cheaper to manufacture

Inkjet
In the inkjet process, liquid photopolymers (synthetic resins) are applied to the building platform in layers through nozzles.
These nozzles work in a similar way to conventional inkjet printers. The material is placed precisely where it is needed. It is applied in very fine layers and hardened using UV light.
The process is particularly suitable for creating precise and detailed models, as it offers high resolution and smooth surfaces.
Advantages
High accuracy and attention to detail
Quick removal of support material
Diversity


Which process is suitable for my application?
Do you already have an application and are unsure which process is right for you?
Talk to us – together we will find the right solution.
Contact form
thinkTEC GmbH | thinkTEC 3D GmbH
Elsenthal 51
94481 Grafenau
Tel.: +49 (0) 8552 974971 – 0
Email: anfrage@thinktec.bayern










